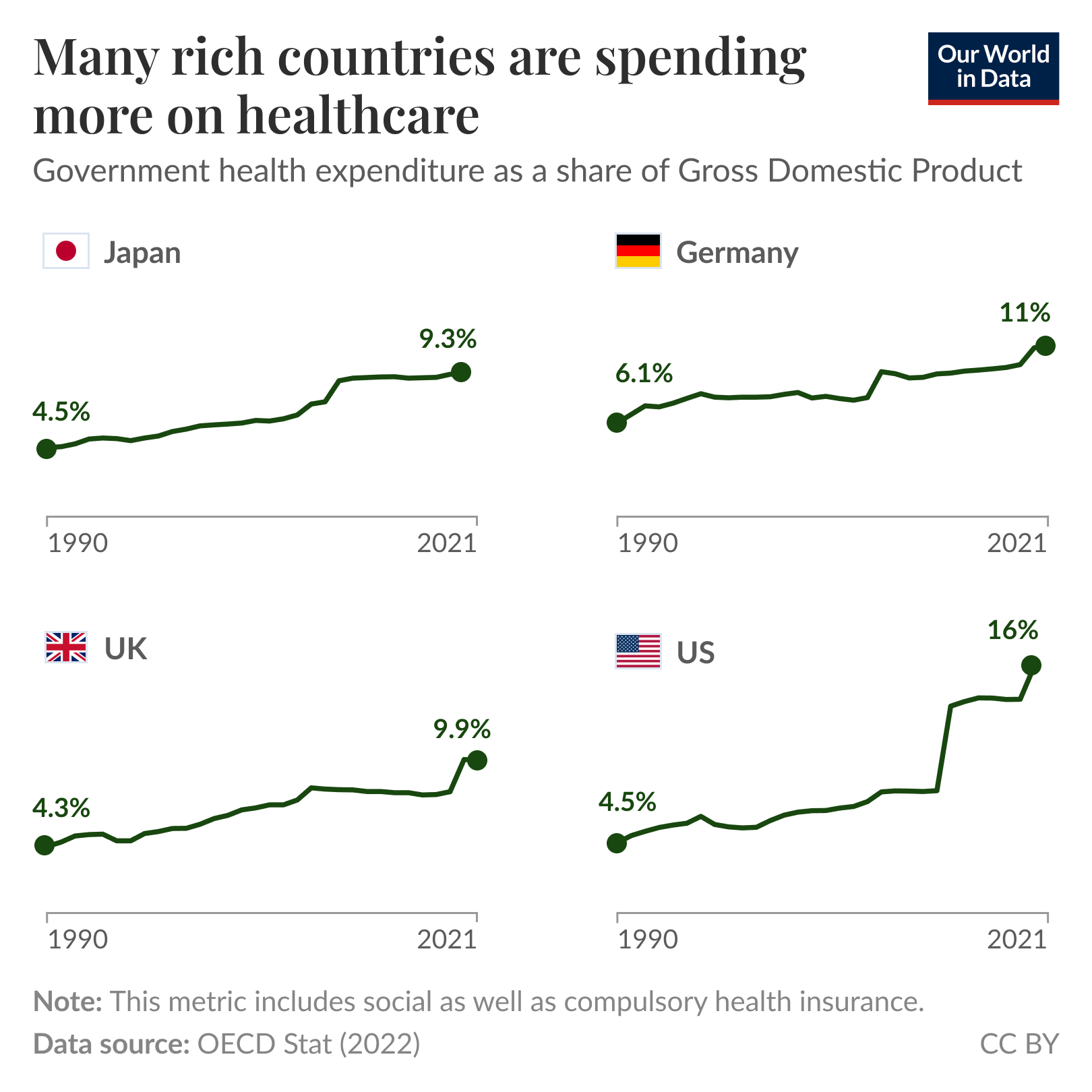
Government spending on health has grown substantially across rich nations since 1990, with particularly steep increases in the United States. The chart shows healthcare spending as a share of gross domestic product (GDP) in four countries.
Japan and the UK saw their share more than double, while it more than tripled in the United States, from 4.5% to 16% of GDP. The rising costs partly reflect demographic change, as older populations typically need more medical care, as well as the COVID-19 pandemic.
Each country organizes healthcare differently. Germany requires everyone to buy insurance from regulated providers, while Japan gives everyone government insurance. The United Kingdom provides healthcare directly through its national health service, while the US combines private insurance with government coverage for the elderly and those on low incomes.
“Data Page: Public health expenditure as a share of GDP”, part of the following publication: Esteban Ortiz-Ospina and Max Roser (2017) - “Healthcare Spending”. Data adapted from OECD Health Expenditure and Financing Database, OECD, Lindert. Retrieved from https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/public-health-expenditure-share-gdp [online resource]






Post comments