1.Augmented reality accurate localization, assisting endoscopic cerebral hematoma removal surgery
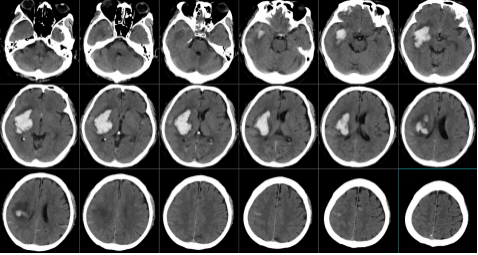
The Department of Neurosurgery (Digital/Secure Neurosurgery) of the East Campus accurately localized a deep hematoma in the brain and completed hematoma removal with the assistance of augmented reality constructed by a smartphone program. The patient is a 63-year-old male who was admitted to the hospital as an emergency with "sudden onset of weakness of the left side of the limbs with slurred speech for 2 hours," and underwent a craniocerebral CT suggesting a cerebral hemorrhage in the right basal ganglia region, with a volume of about 55 ml. The preoperative images are as follows:
The patient was asleep, bilateral pupils were equal in size, light reflex was slow, and the indications for surgery were clear. The neurosurgical team of Du Changwang, chief of department, Liu Yiping and Wang Junmin, deputy chief physicians, and Feng Yanwei, attending physician, decided to adopt the augmented reality precise localization and plan the optimal surgical path, and the small bone window craniotomy endoscopic hematoma removal, which was less traumatic, with fewer complications and quicker recovery.
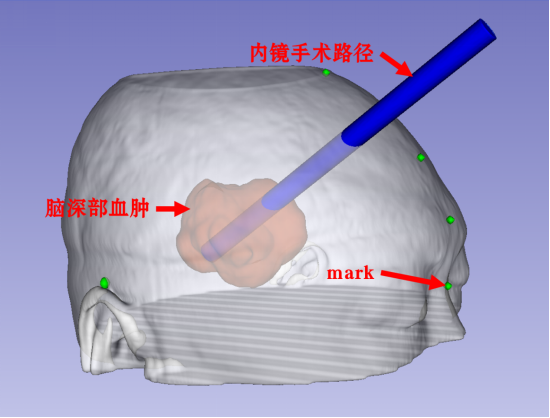
Three-dimensional reconstruction of the patient's head, hematoma, mark point, digital technology to plan the optimal surgical path, as follows

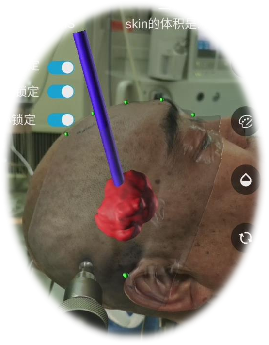
The reconstructed model and the planned optimal surgical path were exported to the smartphone augmented reality software and aligned with the patient's registration, as follows
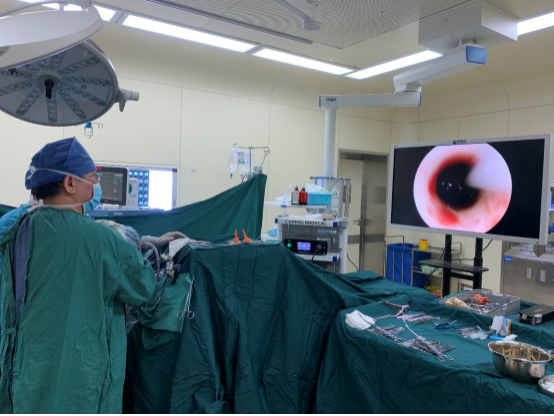
The surgery went smoothly and a bone flap of about 28 mm was taken during the operation, and the flap was repositioned and fixed after the operation, as shown in the figure below.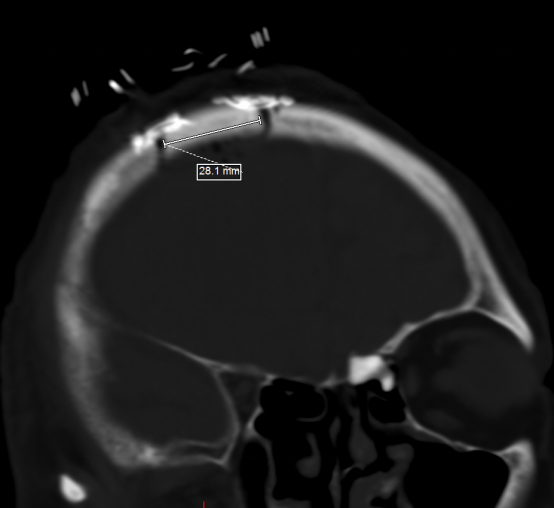
On the first day after the operation, the deep brain hematoma was basically removed completely, and the intracranial pressure was significantly reduced.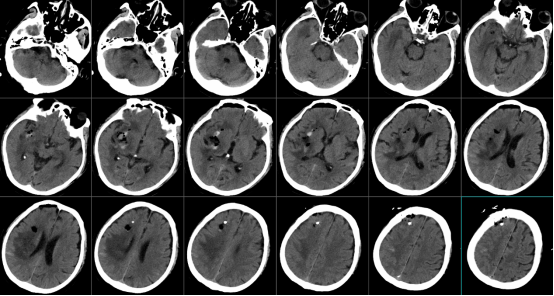
With the improvement of neurosurgical diagnosis and treatment technology, minimally invasive neurosurgery has become more and more important, and neuroendoscopic technology has also been used in the surgical treatment of hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage. The key to neuroendoscopic removal of hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage is to plan the optimal surgical path to completely remove the hematoma while reducing the strain on the surrounding brain tissues. Current research results confirm that augmented reality and mixed reality technology in neurosurgery is a reliable, versatile, and promising tool for precise localization as well as presenting the preoperatively planned surgical path; Neurosurgery Department, East Campus (Digital/Secure Neurosurgery) keeps abreast of the frontiers of medical high technology and applies AR and MR technologies to neurosurgery, improving the safety and effectiveness of neurosurgery.
2.Augmented Reality Precise Positioning Helps Epidural Hematoma Removal Surgery
Recently, the neurosurgery department (digital/secure neurosurgery) of the East Hospital District accurately positioned an epidural hematoma and completed hematoma removal with the assistance of augmented reality constructed by a smartphone program, which is the first time that augmented reality technology has been applied to the clinic in Weibei District. The patient is a 30-year-old male, who was admitted to the hospital as an emergency with a headache caused by a trauma for 3 hours, and a cranial CT showed a right frontotemporal epidural hematoma with a volume of about 50 ml. The preoperative images are as follows: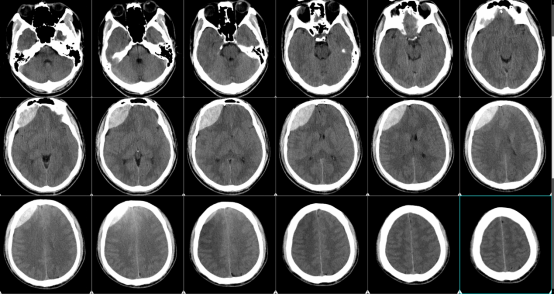
Three-dimensional reconstruction of the patient's skull, hematoma and mark point.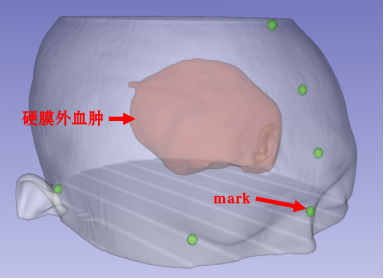
The reconstructed model was exported to the smartphone augmented reality software and aligned with the patient's registration as follows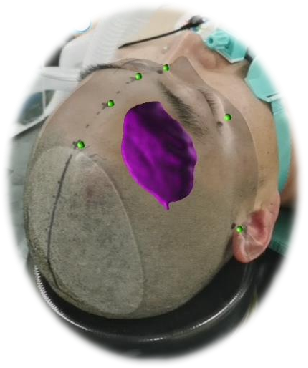
The hematoma was then marked for accurate localization of the cranial surface projection, as follows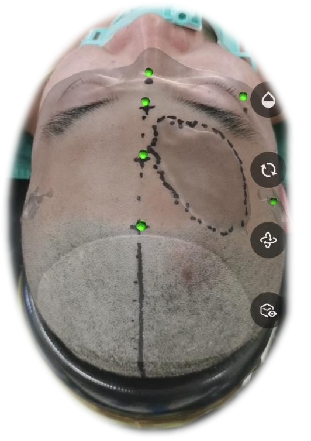
The surgical incision was designed as follows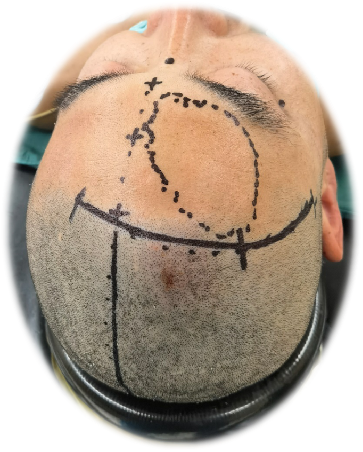
The surgery went smoothly and the patient returned to the ward after he was awake from anesthesia. On the first postoperative day, the CT scan showed that the epidural hematoma had been completely cleared, as follows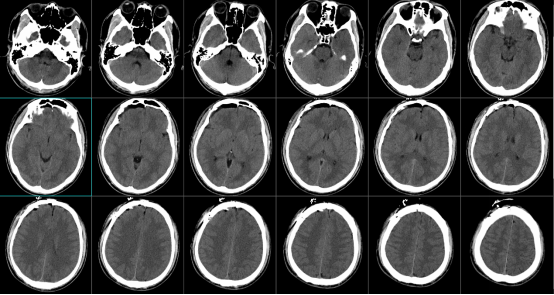
The patient was discharged from the hospital on the third day after surgery.
With the improvement of neurosurgery diagnosis and treatment technology, the status of minimally invasive neurosurgery is increasing. Precise positioning is the foundation of minimally invasive neurosurgery, which reduces unnecessary exposure through precise positioning, practices the concept of minimally invasive, and improves the safety of neurosurgery.
Augmented Reality (AR) technology can superimpose and display computer-generated virtual objects, scenes, etc. onto the real scene in real time, superimposing the virtual world and real objects into the same space in real time, in order to enhance the user's perception of the real world. Mixed Reality (Mixed Reality, MR) technology is a further development on AR technology, which combines the advantages of virtual reality (virtual reality, VR) and AR, and by presenting virtual scene information in the real scene, it builds up an interactive feedback information loop between the real world, the virtual world, and the user, and integrates virtual information with the real world. This creates a new visualization environment in which physical and digital objects coexist and interact in real time.
The application of AR and MR technology in the medical field needs to complete the following three steps: (1) collecting data and constructing 3D virtual models; (2) displaying 3D virtual models; and (3) image registration, i.e., the accurate matching of virtual models with patients.
As science and technology continue to advance, high technology will continue to be applied to the medical field, and current findings confirm that AR and MR technology in neurosurgery is a reliable, versatile, and promising tool; although no prospective randomized studies have been published. The Neurosurgery Department (Digital/Secure Neurosurgery) in the East Campus is keeping abreast of the frontiers of medical high technology by applying AR and MR technologies in surgical procedures, thus improving the safety and effectiveness of neurosurgery.






Post comments