
Image by rawpixel.com on Freepik
Introduction
Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) is recognized as a particularly aggressive and challenging subtype of breast cancer. It is characterized by the absence of three key markers: estrogen receptors, progesterone receptors, and the HER2 protein. This unique profile makes TNBC especially difficult to treat, as conventional therapies that target these receptors, such as hormonal therapies and HER2-targeted treatments, are ineffective. In recent years, significant advancements in the field of immunotherapy have opened up new and exciting avenues for the treatment of TNBC. Among these innovative strategies, neoantigen DNA vaccines have emerged as a particularly promising approach, offering hope for improved patient outcomes.
What are Neoantigens?
Neoantigens are defined as novel protein sequences that arise specifically from mutations found within tumor cells. These antigens are unique to the cancerous cells and are not present in normal, healthy tissues, which makes them ideal targets for cancer immunotherapy. By focusing on neoantigens, the immune system can be trained to specifically recognize and attack cancer cells while sparing the surrounding healthy cells, thereby minimizing collateral damage. This specificity is crucial in developing effective cancer treatments that enhance the body’s natural immune response against tumors.
Neoantigen DNA Vaccines
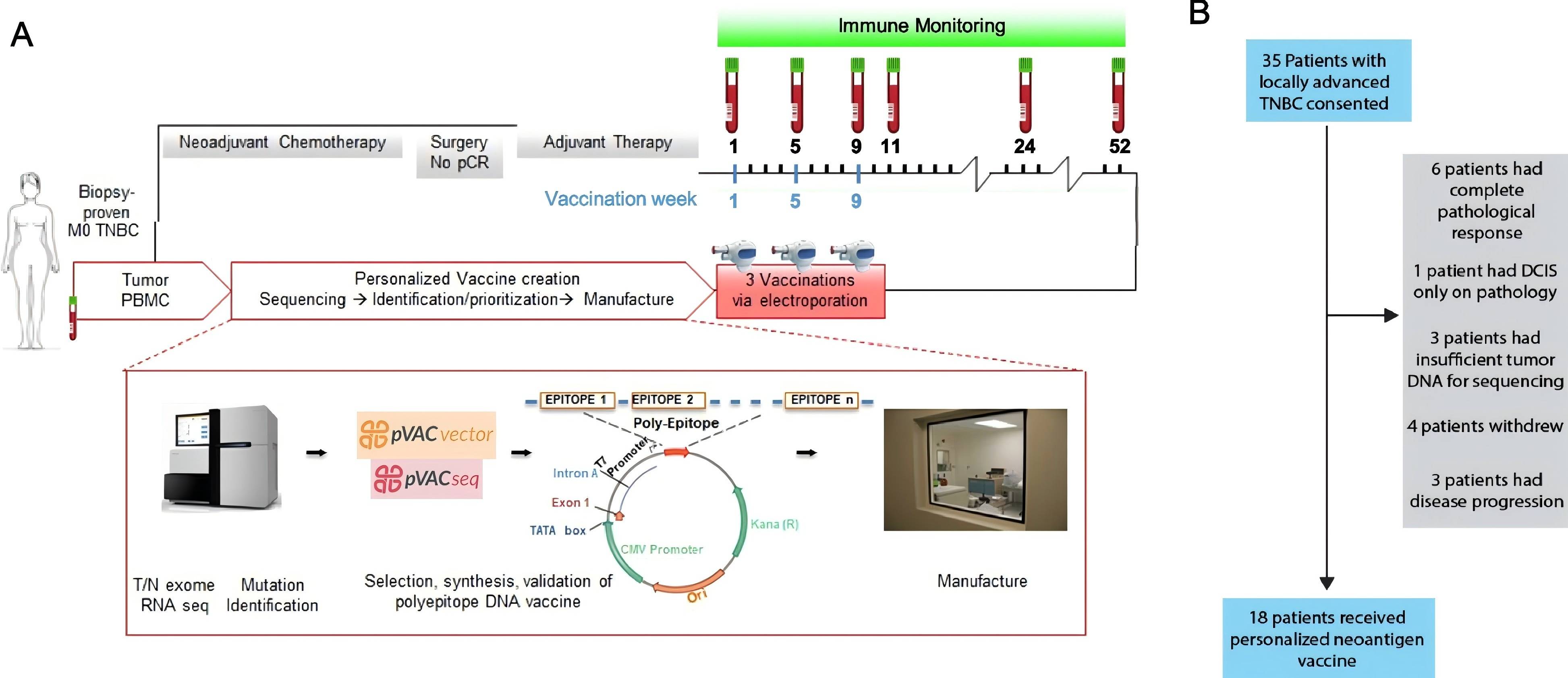
Neoantigen DNA vaccines are a cutting-edge approach that involves the use of DNA sequences that encode for tumor-specific neoantigens. The primary goal of these vaccines is to stimulate the patient’s immune system to recognize and subsequently attack cancer cells that express these neoantigens. The process of creating these vaccines begins with the identification of neoantigens through comprehensive genomic sequencing of the tumor. Once the neoantigens are identified, DNA constructs that encode these specific neoantigens are synthesized. The final step involves delivering this DNA into the patient’s cells, which induces a robust immune response aimed at targeting and eliminating the cancerous cells.
Safety and Feasibility
Clinical studies conducted thus far have demonstrated that neoantigen DNA vaccines are not only safe but also feasible for use in patients diagnosed with TNBC. The vaccines have been shown to be well-tolerated by patients, with minimal adverse effects reported, which is a significant advantage in the context of cancer treatment. The DNA-based approach allows for the rapid and cost-effective production of personalized vaccines that are tailored to each patient’s unique tumor profile. This personalization is a key factor in enhancing the effectiveness of the treatment, as it aligns the immune response with the specific characteristics of the patient’s cancer.
Inducing Neoantigen-Specific Immune Responses
One of the most significant findings emerging from clinical trials is the remarkable ability of neoantigen DNA vaccines to induce robust neoantigen-specific immune responses. Patients who have received these vaccines have shown a notable increase in the activation of neoantigen-specific T cells. These T cells are crucial as they possess the capability to recognize and destroy cancer cells that express the targeted neoantigens. This immune activation is essential for achieving long-term control of the cancer and has the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes. The ability to harness the body’s immune system in this way represents a transformative shift in cancer treatment paradigms.
Case Studies and Clinical Trials
Several compelling case studies and clinical trials have underscored the potential of neoantigen DNA vaccines in the treatment of TNBC. For example, a recent phase I clinical trial demonstrated that patients with advanced TNBC who received neoantigen DNA vaccines exhibited significant immune responses. In some cases, these responses were associated with observable tumor regression, which is a promising indicator of the treatment’s efficacy. These encouraging results have paved the way for larger, more comprehensive studies that aim to further evaluate the effectiveness of this innovative approach. The ongoing research is critical for establishing the role of neoantigen DNA vaccines in standard treatment protocols for TNBC.
Future Directions
The initial success of neoantigen DNA vaccines in early clinical trials suggests a bright and promising future for this therapeutic strategy. Ongoing research efforts are focused on optimizing vaccine design to enhance their effectiveness. Additionally, researchers are exploring improved delivery methods to ensure that the vaccines can be administered in the most effective manner possible. There is also a growing interest in combining neoantigen vaccines with other forms of immunotherapy to create a synergistic effect that could further enhance treatment outcomes. Furthermore, efforts are being made to expand the application of neoantigen vaccines to other cancer types beyond TNBC, which could potentially benefit a broader range of patients.
Conclusion
In conclusion, neoantigen DNA vaccines represent a groundbreaking advancement in the treatment landscape for triple negative breast cancer. Their unique ability to safely and effectively induce neoantigen-specific immune responses offers new hope for patients grappling with this particularly challenging disease. As research continues to progress, it is anticipated that neoantigen DNA vaccines may become a cornerstone of personalized cancer immunotherapy. This would provide tailored and effective treatment options for patients not only with TNBC but potentially with other types of cancer as well, marking a significant step forward in the fight against cancer.
Source: https://genomemedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13073-024-01388-3





Post comments